Difference between revisions of "Detector configuration and scientific potential"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Characteristic strains.png|Sensitivity models of LGWA and its pathfinder mission Soundcheck. The signal spectra represent two months of observation time before merger. Most of the signals experience an amplitude modulation caused by the rotation of the Moon. This modulation together with phase changes connected to the Moon's orbital motion around Earth and Sun allow precise sky-localization.|thumb|600px]] |
The GW observation band of LGWA would span from about 1mHz to a few Hz. Over the lower part of the observation band, sensitivity will be limited by the noise of the seismometer used to read out the surface vibrations. At higher frequencies, it is possible that a seismic background forms a sensitivity limitation. The array configuration will allow us to disentangle lunar seismic events from GW signals, which effectively reduces the seismic background noise. | The GW observation band of LGWA would span from about 1mHz to a few Hz. Over the lower part of the observation band, sensitivity will be limited by the noise of the seismometer used to read out the surface vibrations. At higher frequencies, it is possible that a seismic background forms a sensitivity limitation. The array configuration will allow us to disentangle lunar seismic events from GW signals, which effectively reduces the seismic background noise. | ||
The question about the lunar GW response is not trivial to answer. An intuitive explanation of what happens requires the choice of a coordinate system. For example, in a local Lorentz frame, one must consider the change in coordinates of the seismometer proof mass with respect to the center of mass of the Moon. In this coordinate system, if the Moon did not respond to GWs at all, the seismometer would still see a GW signal since its proof mass would move with respect to an unresponsive lunar surface. Of course, there is a response of the Moon in a local Lorentz frame and it will amplify the GW signal seen by the seismometer at frequencies close to the normal-mode resonances, and it will dilute the GW signals off-resonance. How large the dilution is off-resonance has great influence on the overall GW response of the Moon, and it depends on geological details. Normal-mode simulations will provide more accurate models in the future. | The question about the lunar GW response is not trivial to answer. An intuitive explanation of what happens requires the choice of a coordinate system. For example, in a local Lorentz frame, one must consider the change in coordinates of the seismometer proof mass with respect to the center of mass of the Moon. In this coordinate system, if the Moon did not respond to GWs at all, the seismometer would still see a GW signal since its proof mass would move with respect to an unresponsive lunar surface. Of course, there is a response of the Moon in a local Lorentz frame and it will amplify the GW signal seen by the seismometer at frequencies close to the normal-mode resonances, and it will dilute the GW signals off-resonance. How large the dilution is off-resonance has great influence on the overall GW response of the Moon, and it depends on geological details. Normal-mode simulations will provide more accurate models in the future. | ||
| − | Taking a more optimistic view on the LGWA sensitivity, it will be able to see a few binaries of neutron stars and solar-mass black holes together with mergers of massive black-hole binaries and many detections of white-dwarf binaries. Even though the detection of neutron star binaries would be rare, these would be observations of great importance since they would be used to issue alerts of an impending merger of these systems with precise sky location, which would allow the astronomers with EM facilities to prepare for these events. | + | Taking a more optimistic view on the LGWA sensitivity, it will be able to see a few binaries of neutron stars and solar-mass black holes together with mergers of massive black-hole binaries and many detections of white-dwarf binaries. Even though the detection of neutron star binaries would be rare, these would be observations of great importance since they would be used to issue alerts of an impending merger of these systems with precise sky location, which would allow GW scientists and the astronomers with EM facilities to prepare for these events. |
Latest revision as of 19:27, 11 July 2023
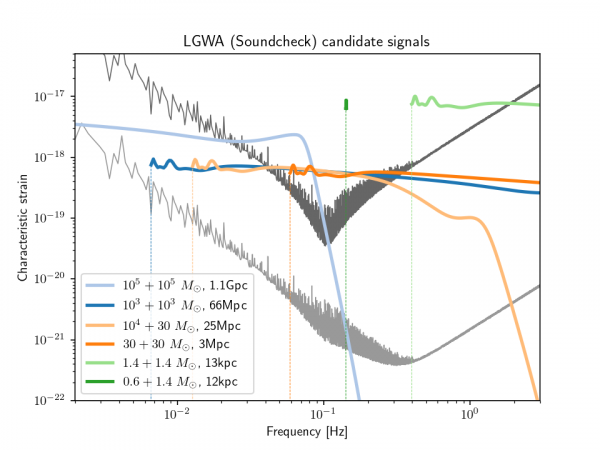
The GW observation band of LGWA would span from about 1mHz to a few Hz. Over the lower part of the observation band, sensitivity will be limited by the noise of the seismometer used to read out the surface vibrations. At higher frequencies, it is possible that a seismic background forms a sensitivity limitation. The array configuration will allow us to disentangle lunar seismic events from GW signals, which effectively reduces the seismic background noise.
The question about the lunar GW response is not trivial to answer. An intuitive explanation of what happens requires the choice of a coordinate system. For example, in a local Lorentz frame, one must consider the change in coordinates of the seismometer proof mass with respect to the center of mass of the Moon. In this coordinate system, if the Moon did not respond to GWs at all, the seismometer would still see a GW signal since its proof mass would move with respect to an unresponsive lunar surface. Of course, there is a response of the Moon in a local Lorentz frame and it will amplify the GW signal seen by the seismometer at frequencies close to the normal-mode resonances, and it will dilute the GW signals off-resonance. How large the dilution is off-resonance has great influence on the overall GW response of the Moon, and it depends on geological details. Normal-mode simulations will provide more accurate models in the future.
Taking a more optimistic view on the LGWA sensitivity, it will be able to see a few binaries of neutron stars and solar-mass black holes together with mergers of massive black-hole binaries and many detections of white-dwarf binaries. Even though the detection of neutron star binaries would be rare, these would be observations of great importance since they would be used to issue alerts of an impending merger of these systems with precise sky location, which would allow GW scientists and the astronomers with EM facilities to prepare for these events.